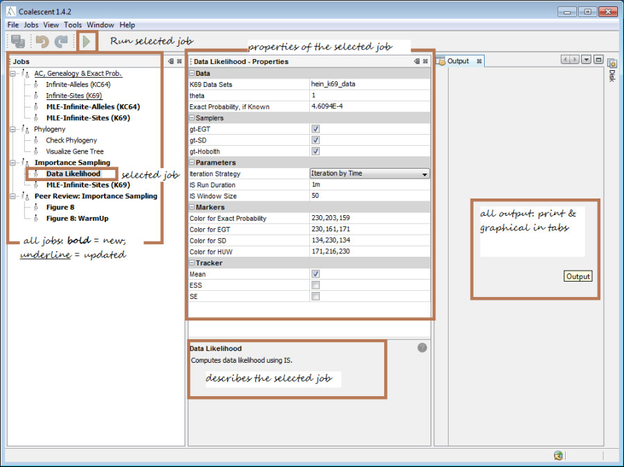
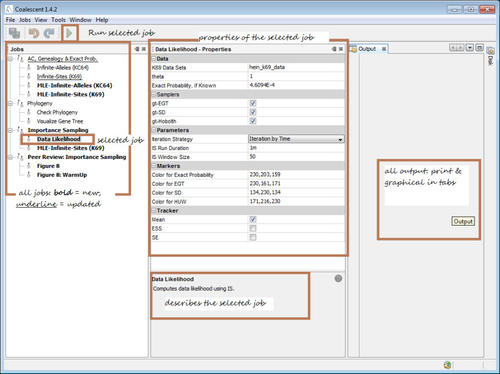
System Requirementscoalescent is supported only on 64 bit platforms (Windows, Mac-OS-X, Linux) as it involves intensive computation. While 64 bit platforms allow larger memory space, they also consume twice as much memory (compared to 32 bit systems), simply to store a larger address space. This is a well known trade-off.
Jobs would require different amounts of memory depending on various factors but 4 GB of dedicated memory to the underlying Java Virtual Machine (JVM) process would be sufficient for running all the jobs. The dedicated memory to the JVM is allocated during program launch and is typically set to 1/4th of the system`s free memory. If your system does not have enough free memory, the program may become unresponsive for computationally demanding jobs. If the system has enough free memory (say, 8GB) but that would only allocate around 2GB of dedicated memory, you can allocate the required memory manually. Go to INSTALL-DIRECTORY/etc/coalescent.conf and edit the following:
change the line
default_options="--branding coalescent -J-Xms24m"
to
default_options="--branding coalescent -J-Xms24m –J-Xmx4000m"
|